B. Peng, S. K. Ozdemir, S. Rotter, H. Yilmaz, M. Liertzer, F. Monifi, C. M. Bender, F. Nori, L. Yang
Controlling and reversing the effects of loss are major challenges in optical systems. For lasers losses need to be overcome by a sufficient amount of gain to reach the lasing threshold. We show how to turn losses into gain by steering the parameters of a system to the vicinity of an exceptional point (EP), which occurs when the eigenvalues and the corresponding eigenstates of a system coalesce. In our system of coupled microresonators, EPs are manifested as the loss-induced suppression and revival of lasing. Below a critical value, adding loss annihilates an existing Raman laser. Beyond this critical threshold, lasing recovers despite the increasing loss, in stark contrast to what would be expected from conventional laser theory. Our results exemplify the counterintuitive features of EPs and present an innovative method for reversing the effect of loss.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1410.7474
Optics (physics.optics); Quantum Physics (quant-ph)
M. Brandstetter, M. Liertzer, C. Deutsch, P. Klang, J. Schöberl, H. E. Türeci, G. Strasser, K. Unterrainer, S. Rotter
When two resonant modes in a system with gain or loss coalesce in both their resonance position and their width, a so-called “Exceptional Point” occurs which acts as a source of non-trivial physics in a diverse range of systems. Lasers provide a natural setting to study such “non-Hermitian degeneracies”, since they feature resonant modes and a gain material as their basic constituents. Here we show that Exceptional Points can be conveniently induced in a photonic molecule laser by a suitable variation of the applied pump. Using a pair of coupled micro-disk quantum cascade lasers, we demonstrate that in the vicinity of these Exceptional Points the laser shows a characteristic reversal of its pump-dependence, including a strongly decreasing intensity of the emitted laser light for increasing pump power. This result establishes photonic molecule lasers as promising tools for exploring many further fascinating aspects of Exceptional Points, like a strong line-width enhancement and the coherent perfect absorption of light in their vicinity as well as non-trivial mode-switching and the accumulation of a geometric phase when encircling an Exceptional Point parametrically.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1404.1837
Optics (physics.optics); Mesoscale and Nanoscale Physics (cond-mat.mes-hall); Chaotic Dynamics (nlin.CD)
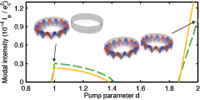 M. Liertzer, Li Ge, A. Cerjan, A. D. Stone, H. E. Türeci, S. Rotter
M. Liertzer, Li Ge, A. Cerjan, A. D. Stone, H. E. Türeci, S. Rotter
We demonstrate that the above-threshold behavior of a laser can be strongly affected by exceptional points which are induced by pumping the laser non-uniformly. At these singularities the eigenstates of the non-Hermitian operator which describes the lasing modes coalesce. In the vicinity of these points the laser may turn off even when the overall pump power deposited in the system is increased. We suggest that such signatures of a pump-induced exceptional point can be experimentally probed with coupled ridge or microdisk lasers.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1109.0454
Optics (physics.optics)
http://arxiv.org/abs/1109.0454
