Carl M. Bender, Daniel W. Hook
Classical mechanics is a singular theory in that real-energy classical particles can never enter classically forbidden regions. However, if one regulates classical mechanics by allowing the energy E of a particle to be complex, the particle exhibits quantum-like behavior: Complex-energy classical particles can travel between classically allowed regions separated by potential barriers. When Im(E) -> 0, the classical tunneling probabilities persist. Hence, one can interpret quantum tunneling as an anomaly. A numerical comparison of complex classical tunneling probabilities with quantum tunneling probabilities leads to the conjecture that as ReE increases, complex classical tunneling probabilities approach the corresponding quantum probabilities. Thus, this work attempts to generalize the Bohr correspondence principle from classically allowed to classically forbidden regions.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1011.0121
High Energy Physics – Theory (hep-th); Mathematical Physics (math-ph); Quantum Physics (quant-ph)
Carl M. Bender, R. J. Kalveks
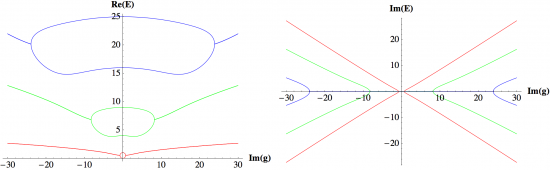
The E2 algebra has three elements, J, u, and v, which satisfy the commutation relations [u,J]=iv, [v,J]=-iu, [u,v]=0. We can construct the Hamiltonian H=J^2+gu, where g is a real parameter, from these elements. This Hamiltonian is Hermitian and consequently it has real eigenvalues. However, we can also construct the PT-symmetric and non-Hermitian Hamiltonian H=J^2+igu, where again g is real. As in the case of PT-symmetric Hamiltonians constructed from the elements x and p of the Heisenberg algebra, there are two regions in parameter space for this PT-symmetric Hamiltonian, a region of unbroken PT symmetry in which all the eigenvalues are real and a region of broken PT symmetry in which some of the eigenvalues are complex. The two regions are separated by a critical value of g.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1009.3236
High Energy Physics – Theory (hep-th); Mathematical Physics (math-ph); Quantum Physics (quant-ph)
Peter N. Meisinger, Michael C. Ogilvie, Timothy D. Wiser
 Generalized PT symmetry provides crucial insight into the sign problem for two classes of models. In the case of quantum statistical models at non-zero chemical potential, the free energy density is directly related to the ground state energy of a non-Hermitian, but generalized PT-symmetric Hamiltonian. There is a corresponding class of PT-symmetric classical statistical mechanics models with non-Hermitian transfer matrices. For both quantum and classical models, the class of models with generalized PT symmetry is precisely the class where the complex weight problem can be reduced to real weights, i.e., a sign problem. The spatial two-point functions of such models can exhibit three different behaviors: exponential decay, oscillatory decay, and periodic behavior. The latter two regions are associated with PT symmetry breaking, where a Hamiltonian or transfer matrix has complex conjugate pairs of eigenvalues. The transition to a spatially modulated phase is associated with PT symmetry breaking of the ground state, and is generically a first-order transition. In the region where PT symmetry is unbroken, the sign problem can always be solved in principle. Moreover, there are models with PT symmetry which can be simulated for all parameter values, including cases where PT symmetry is broken.
Generalized PT symmetry provides crucial insight into the sign problem for two classes of models. In the case of quantum statistical models at non-zero chemical potential, the free energy density is directly related to the ground state energy of a non-Hermitian, but generalized PT-symmetric Hamiltonian. There is a corresponding class of PT-symmetric classical statistical mechanics models with non-Hermitian transfer matrices. For both quantum and classical models, the class of models with generalized PT symmetry is precisely the class where the complex weight problem can be reduced to real weights, i.e., a sign problem. The spatial two-point functions of such models can exhibit three different behaviors: exponential decay, oscillatory decay, and periodic behavior. The latter two regions are associated with PT symmetry breaking, where a Hamiltonian or transfer matrix has complex conjugate pairs of eigenvalues. The transition to a spatially modulated phase is associated with PT symmetry breaking of the ground state, and is generically a first-order transition. In the region where PT symmetry is unbroken, the sign problem can always be solved in principle. Moreover, there are models with PT symmetry which can be simulated for all parameter values, including cases where PT symmetry is broken.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1009.0745
High Energy Physics – Theory (hep-th)

