Pijush K. Ghosh
Examples of non-hermitian quantum systems admitting topological insulator phase are presented in one, two and three space dimensions. All of these non-hermitian Hamiltonians have entirely real bulk eigenvalues and unitarity is maintained with the introduction of appropriate inner-products in the corresponding Hilbert spaces. The topological invariant characterizing a particular phase is shown to be identical for a non-hermitian Hamiltonian and its hermitian counterpart, to which it is related through a non-unitary similarity transformation. A classification scheme for topological insulator phases in pseudo-hermitian quantum systems is suggested.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1109.1697
Quantum Physics (quant-ph); High Energy Physics – Theory (hep-th)
Mario Kieburg, Jacobus J.M. Verbaarschot, Savvas Zafeiropoulos
We find the lattice spacing dependence of the eigenvalue density of the non-Hermitian Wilson Dirac operator in the \(\epsilon\)-domain. The starting point is the joint probability density of the corresponding random matrix theory. In addition to the density of the complex eigenvalues we also obtain the density of the real eigenvalues separately for positive and negative chiralities as well as an explicit analytical expression for the number of additional real modes.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1109.0656
High Energy Physics – Lattice (hep-lat); High Energy Physics – Theory (hep-th); Mathematical Physics (math-ph)
Fabio Bagarello, Miloslav Znojil
The increasingly popular concept of a hidden Hermiticity of operators (i.e., of their Hermiticity with respect to an {\it ad hoc} inner product in Hilbert space) is compared with the recently introduced notion of {\em non-linear pseudo-bosons}. The formal equivalence between these two notions is deduced under very general assumptions. Examples of their applicability in quantum mechanics are discussed.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1109.0605
Mathematical Physics (math-ph); Functional Analysis (math.FA); Quantum Physics (quant-ph)
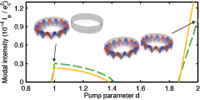 M. Liertzer, Li Ge, A. Cerjan, A. D. Stone, H. E. Türeci, S. Rotter
M. Liertzer, Li Ge, A. Cerjan, A. D. Stone, H. E. Türeci, S. Rotter
We demonstrate that the above-threshold behavior of a laser can be strongly affected by exceptional points which are induced by pumping the laser non-uniformly. At these singularities the eigenstates of the non-Hermitian operator which describes the lasing modes coalesce. In the vicinity of these points the laser may turn off even when the overall pump power deposited in the system is increased. We suggest that such signatures of a pump-induced exceptional point can be experimentally probed with coupled ridge or microdisk lasers.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1109.0454
Optics (physics.optics)
http://arxiv.org/abs/1109.0454
Tomas Azizov, Carsten Trunk
In the recent years a generalization \(H=p^2 +x^2(ix)^\epsilon\) of the harmonic oscillator using a complex deformation was investigated, where \(\epsilon\) is a real parameter. Here, we will consider the most simple case: \(\epsilon\) even and \(x\) real. We will give a complete characterization of three different classes of operators associated with the differential expression H: The class of all self-adjoint (Hermitian) operators, the class of all PT symmetric operators and the class of all P-self-adjoint operators. Surprisingly, some of the PT symmetric operators associated to this expression have no resolvent set.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1108.5923
Quantum Physics (quant-ph)
Yogesh N. Joglekar, Jacob L. Barnett
By investigating a parity and time-reversal (PT) symmetric, $N$-site lattice with impurities \(\pm i\gamma\) and hopping amplitudes \(t_0 (t_b)\) for regions outside (between) the impurity locations, we probe the origin of maximal PT-symmetry breaking that occurs when the impurities are nearest neighbors. Through a simple and exact derivation, we prove that the critical impurity strength is equal to the hopping amplitude between the impurities, \(\gamma_c=t_b\), and the simultaneous emergence of \(N\) complex eigenvalues is a robust feature of any PT-symmetric hopping profile. Our results show that the threshold strength \(\gamma_c\) can be widely tuned by a small change in the global profile of the lattice, and thus have experimental implications.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1108.6083
Quantum Physics (quant-ph); Statistical Mechanics (cond-mat.stat-mech)
Yusef Maleki
In this parer, q-deformed oscillator for pseudo-Hermitian systems is investigated and pseudo-Hermitian appropriate coherent and squeezed states are studied. Also, some basic properties of these states is surveyed. The over-completeness property of the para-Grassmannian pseudo-Hermitian coherent states (PGPHCSs) examined, and also the stability of coherent and squeezed states discussed. The pseudo-Hermitian supercoherent states as the product of a pseudo-Hermitian bosonic coherent state and a para-Grassmannian pseudo-Hermitian coherent state introduced, and the method also developed to define pseudo-Hermitian supersqueezed states. It is also argued that, for q-oscillator algebra of \(k+1\) degree of nilpotency based on the changed ladder operators, defined in here, we can obtain deformed \(SU_{q^2}(2)\) and \(SU_{q^{2k}}(2)\) and also \(SU_{q^{2k}}(1,1)\). Moreover, the entanglement of multi-level para-Grassmannian pseudo-Hermitian coherent state will be considered. This is done by choosing an appropriate weight function, and integrating over tensor product of PGPHCSs.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1108.5005
Mathematical Physics (math-ph); High Energy Physics – Theory (hep-th); Quantum Physics (quant-ph)
D. Krejcirik, P. Siegl, J. Zelezny
We consider one-dimensional Schroedinger-type operators in a bounded interval with non-self-adjoint Robin-type boundary conditions. It is well known that such operators are generically conjugate to normal operators via a similarity transformation. Motivated by recent interests in quasi-Hermitian Hamiltonians in quantum mechanics, we study properties of the transformations in detail. We show that they can be expressed as the sum of the identity and an integral Hilbert-Schmidt operator. In the case of parity and time reversal boundary conditions, we establish closed integral-type formulae for the similarity transformations, derive the similar self-adjoint operator and also find the associated “charge conjugation” operator, which plays the role of fundamental symmetry in a Krein-space reformulation of the problem.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1108.4946
Spectral Theory (math.SP); Mathematical Physics (math-ph); Functional Analysis (math.FA); Quantum Physics (quant-ph)
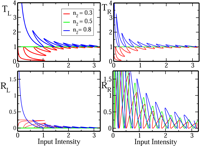 Zin Lin, Hamidreza Ramezani, Toni Eichelkraut, Tsampikos Kottos, Hui Cao, Demetrios N. Christodoulides
Zin Lin, Hamidreza Ramezani, Toni Eichelkraut, Tsampikos Kottos, Hui Cao, Demetrios N. Christodoulides
We show that parity-time (PT) symmetric Bragg periodic structures, near the spontaneous PT – symmetry breaking point, can act as unidirectional invisible media. In this regime, the re flection from one end is diminished while it is enhanced from the other. At the same time the transmission coefficient and phase, are indistinguishable from those expected in the absence of a grating. The phenomenon is robust even in the presence of Kerr non-linearities, and it can also eff?ectively suppress optical bistabilities.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1108.2493
Optics (physics.optics)
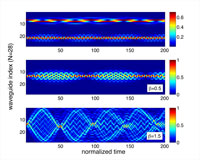 Harsha Vemuri, Vaibhav Vavilala, Theja Bhamidipati, Yogesh N. Joglekar
Harsha Vemuri, Vaibhav Vavilala, Theja Bhamidipati, Yogesh N. Joglekar
Recently, waveguide lattices with non-uniform tunneling have been explored due to their myriad tunable properties, many of which arise from the extended nature of their eigenstates. Here, we investigate the dynamics, localization, and parity- and time-reversal-(PT) symmetry breaking in lattices with only localized eigenstates. We propose three families of tunneling profiles that lead to qualitatively different single-particle time evolution, and show that the effects of weak disorder contain signatures of the localized or extended nature of clean-lattice eigenstates. Our results suggest that waveguide lattices with only localized eigenstates will exhibit a wide array of phenomena that are absent in traditional systems.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1108.1402
Optics (physics.optics); Quantum Gases (cond-mat.quant-gas); Quantum Physics (quant-ph)


